In the world of computer networks there are many terms and concepts. Throughout some articles that we have published on Pplware, we have tried to explain some of these terms/concepts so that our readers are more contextualized with the area of data networks. Do you know what physical addresses and logical addresses are?
Relativamente à questão colocada neste artigo, a resposta é bastante simples. No âmbito das redes informáticas, quando falamos em endereço físico estamo-nos a referir ao endereço MAC (associado à placa de rede) e quando falamos em endereço lógico é o endereço IP (configurado na placa de rede).
ENDEREÇOS FÍSICOS
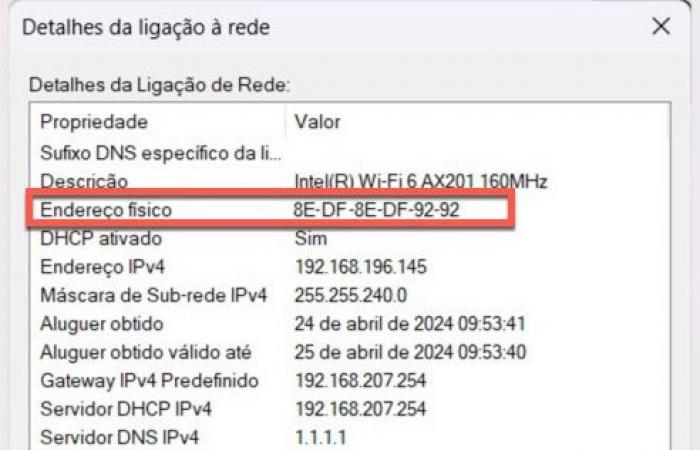
O endereço MAC (Media Access Control) é definido como sendo um endereço físico de uma placa de rede, e é composto por 48 bits (12 caracteres hexadecimais). Os primeiros seis caracteres identificam o fabricante (ex. Intel, surecom, broadcom, etc) e os restantes seis identificam a placa em si.
O endereço MAC é único no mundo para cada placa de rede (apesar de existirem ferramentas que possibilitam a alteração do mesmo), e é mantido na memória ROM, sendo posteriormente essa informação copiada para a memória RAM aquando da inicialização da placa. Há várias formas de representar um endereço MAC:
00-22-18-FB-7A-12 0022.18FB.7A12 00:22:18:FB:7A:12
To view the MAC associated with your card (in Windows), you can access its properties and check the Physical Address field.
For those who want to observe the MAC Address through the Windows command line, you can type: ipconfig /all or getmac. On MacOS and Linux you can use the ifconfig or ip a command.

LOGICAL ADDRESSES
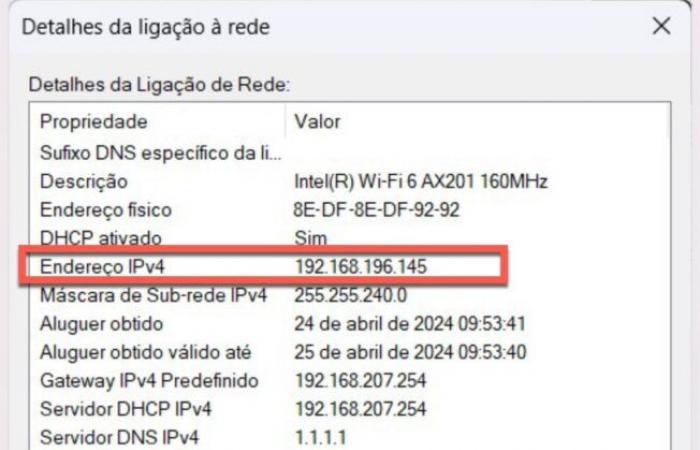
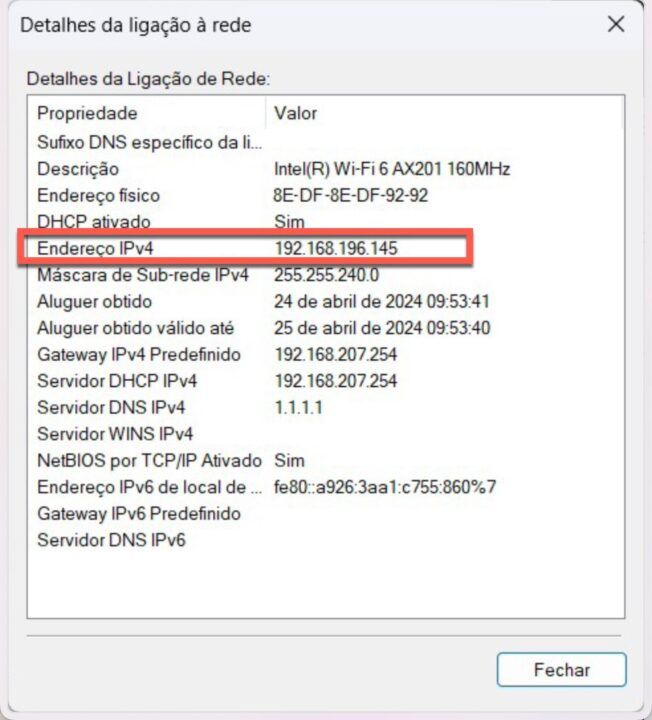
When we talk about addresses in the area of networks, it is normal to immediately associate them with the IP address configured on a network card. The IP address (version 4) is a logical address defined by 32 bits (4 octets) and identifies a device on a given network. IPv6 logical addresses are made up of 128 bits, presented in 8 groups of 4 hexadecimal digits separated by ':' (e.g. 1234:5678:90AB:CDEF:FEDC:BA09:8765:4321).
Regarding IP addresses, there are public addresses and private addresses. Most IP addresses are public, thus allowing our networks (or at least our router that forms the border between our network and the Internet or other networks) to be publicly accessible via the Internet, from anywhere. IP addresses are represented as follows:
192.168.10.1 2.83.6.2 10.10.10.1
To be able to view the IP associated with your card (in Windows) you can access its properties and check the IPv4 Address field or in version 6 of the IP protocol IPv6 Address.
IP address works at layer 3 (network layer) in the OSI model, while MacAddress works at layer 2 (link layer) in the OSI model. For those who want to know more about the OSI model, you can take a look at our article Do you know what the OSI model is?
IN SUMMARY…
Taking advantage of what has already been mentioned, when we talk about physical addresses we are referring to the MAC address. On the other hand, the logical address is the IP address configured on a network card.
I would like to take this opportunity to leave a “challenge” to our readers. What other topics would you like to see covered here in the context of computer networks?