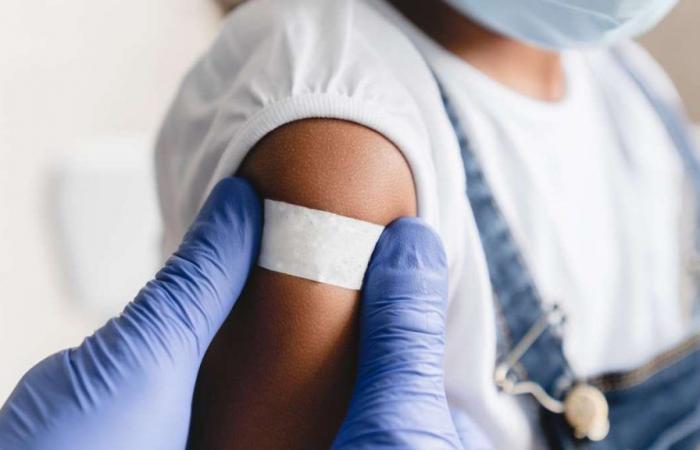
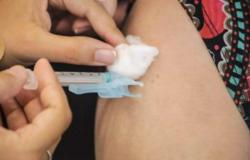
Meningitis, an inflammation of the meninges – the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord – can be caused by various infectious agents, such as viruses, bacteria and fungi. Its symptoms, which include high fever, severe headache and stiff neck, require immediate medical attention as the disease can be serious and lead to serious complications.
World Day to Combat Meningitis
World Meningitis Day, celebrated on April 24, serves as a reminder of the importance of raising awareness about this disease and its prevention.
This date was established in 2009 by the World Federation of Infectious Disease Societies (WFIDS) together with the World Health Organization (WHO), with the aim of joining efforts to reduce the incidence and mortality from meningitis.
What is Meningitis? What are your Types?
World Meningitis Day: what it is, prevention and awareness!
Photo: Cinemafootage Visuals
Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It can be caused by viruses, bacteria or other infectious agents. This is exactly why it is classified according to the causative agent:
- Bacterial meningitis: caused by bacteria, it is the most serious form and requires immediate antibiotic treatment.
- Viral meningitis: caused by a virus, it is generally less serious than bacterial meningitis and can resolve without specific treatment.
- Fungal meningitis: caused by fungi, it is rare and usually affects people with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms of meningitis can vary depending on the type and severity of the disease, but some common warning signs include:
- High fever
- Intense headache
- Stiffness in the neck
- Nausea and vomiting
- Mental confusion
- Somnolence
- Seizures (in severe cases)
Causes and risk factors
World Meningitis Day: what it is, prevention and awareness!
Photo: Inside Creative House
The causes of meningitis vary depending on the type:
- Bacterial meningitis: transmitted by close contact with respiratory secretions or saliva from infected people. Risk factors include:
Age: children under 5 and teenagers are more likely.
Chronic diseases: Diabetes, kidney disease and immunodeficiencies increase the risk.
Conditions that facilitate the entry of bacteria into the meninges: head injuries, birth defects and surgeries.
- Viral meningitis: transmitted by contact with respiratory secretions from infected people. Risk factors include:
Seasons: more common in winter and spring.
Age: children and teenagers are more likely.
Crowds: daycares, schools and dormitories increase the risk.
- Fungal meningitis: It generally affects people with a weakened immune system, such as patients taking immunosuppressants or with serious illnesses.
Prevention
World Meningitis Day: what it is, prevention and awareness!
Photo: Jovanmandic
A vaccination is the most important preventive measure against bacterial meningitis. Several vaccines are available to protect against different types of bacteria, such as meningococcal C, pneumococcal and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib).
Other preventive measures include:
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water.
- Avoid close contact with sick people.
- Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- Do not share personal objects, such as glasses, cutlery and hygiene utensils.
- Maintain ventilated environments and avoid crowds in closed places.
Diagnosis and treatment
The diagnosis of meningitis is made through clinical examinations, blood tests and imaging tests, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the skull. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the disease:
- Bacterial meningitis: treatment with intravenous antibiotics for 7 to 10 days.
- Viral meningitis: It usually does not require specific treatment, just symptomatic support to alleviate symptoms.
- Fungal meningitis: treatment with oral or intravenous antifungals for several weeks or months.
Global and local impact
Meningitis represents a serious challenge to global public health, with an estimated annual death toll of 500,000, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). The disease has a high prevalence in countries in Sub-Saharan Africa, the “Meningitis Belt” region, and in Southeast Asian countries. In Brazil, the incidence of meningitis varies according to the type and region, but the disease represents a public health problem, especially for children and adolescents.
To face the challenge of meningitis, it is essential to invest in effective prevention and treatment measures, such as expanding vaccination coverage, improving access to diagnosis and treatment, in addition to promoting health education.
The Importance of awareness and education
Raising awareness about meningitis and its dangers is essential for the success of measures to prevent and control the disease. Health information and education campaigns must be carried out continuously, using accessible language and targeted at different audiences, including health professionals, local communities and schools. By joining efforts, it is possible to solve the problem.
Source: WHO
Source: Redação Terra Você
Tags: prevention awareness
--