DNA is the fundamental molecule of the human body, transporting genetic information and being responsible for the characteristics that make each human being unique and distinguishable from the rest. Since its discovery in 1953, DNA has been at the epicenter of much research that seeks to unravel the complete sequence of the material contained within it, looking for which part of the molecule responds to each human character and focusing on the development of personalized medicine.
Although DNA is a truly essential part of life, there are some aspects that are still little known. From the striking similarity that exists between human beings to the immense length of the nucleotide chain, DNA is full of curiosities that invite us to marvel and reflect on the complexity and, at the same time, the diversity and beauty of life. .
HUMANS SHARE 99.9% OF THEIR DNA
Yes, although at first glance it may seem like a far-fetched number, all human beings share almost 99.9% of our DNA. In fact, this incredible genetic similarity is the basis of our species, with only the remaining 0.1% responsible for the individual variations that make us unique. However, the influence of the environment It is also an element to consider: environmental factors such as diet, lifestyle and other habits can have a significant impact on our biology, even when we share such a large number of genes.
And it doesn’t end here: despite being very different from chimpanzees, with whom we share 98% of our DNA, our connection to the plant kingdom is also surprisingly close: the percentage we share with a cabbage is between 40% and 50%all due to the evolutionary continuity that connects all forms of life on our planet.
THE LARGE VOLUME OF THE GENOME
Have you ever stopped to think about the size of the genome? In the case of a human woman, with 46 XX chromosomes, her genome is approximately 12,859,525,002 nucleotides. On the other hand, in the case of a man with 46 chromosomes and an XY karyotype, this value is a little smaller, but equally colossal: 12,661,898,042 nucleotides. In other words, if we imagine each of these nucleotides as a letter in a school book, the human genome would occupy around 8.5 million pages: something like a library with more than 8,500 books!
But this enormous pool of genetic information is not just a random accumulation of data: this DNA contains between 20,000 and 25,000 genes that encode the essential instructions for the development, functioning and reproduction of human beings. It is important to note that it is precisely this vast amount of genetic information that reflects the complexity and diversity so characteristic of our species.
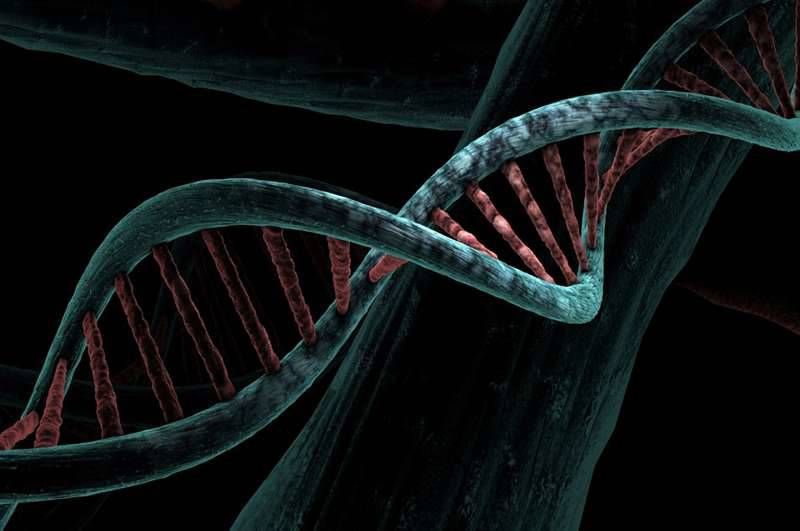

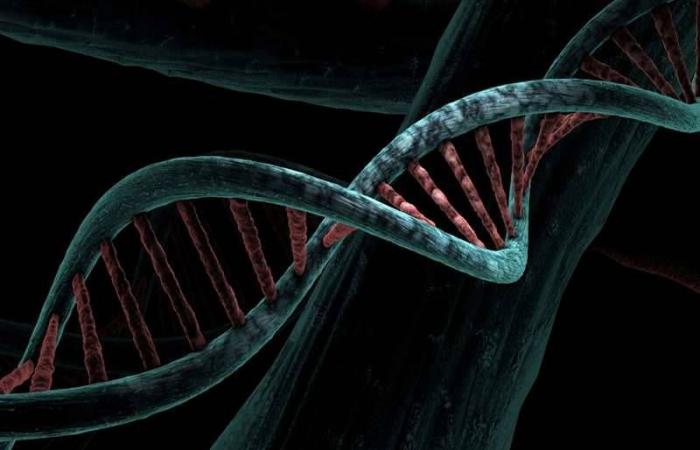
Representation of a DNA chain.
THE NEANDERTAL LEGACY IN DNA
Human beings carry something like a book of their history in their DNA. In the genetic material of the cell nucleus we can find a testimony to our evolutionary past: between 1% and 4% would be shared with Neanderthalsa species close but distinct from Homo sapiens which became extinct hundreds of thousands of years ago. This discovery reveals that, at some point in history, the Homo sapiens and Neanderthals shared the same territory and the same common ancestor, leaving a genetic mark that persists in our species.
Recent investigations have deepened the role of these genes in our biology, showing that they even have some relevance in our immune system and other aspects of our biology. Specifically, a study carried out at Cornell University used genetic data from the UK Biobank, identifying up to 235,000 genetic variants of possible Neanderthal origin. Of these, around 4,300 appear to be linked to human characteristics related to metabolism, development or the immune system.
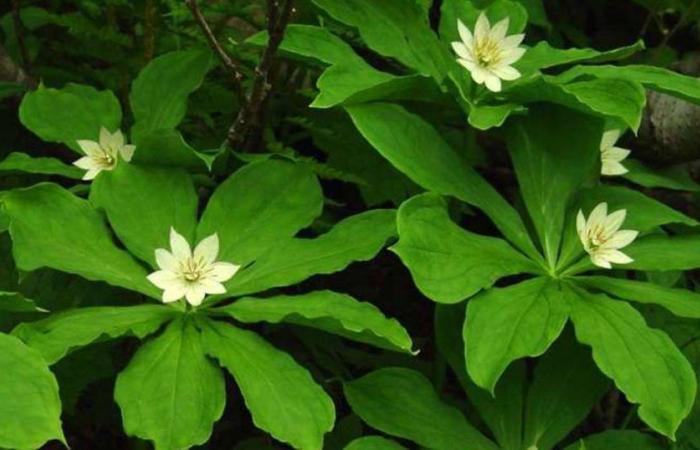
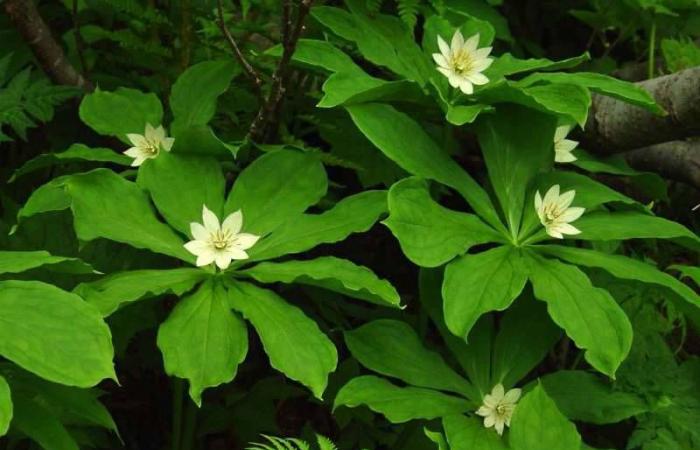
THE DNA OF PARIS JAPONICA
And did you know that there is a flower whose genome is 50 times larger than that of a human being? This is the Japanese Paris, a species of white plant originating from Japan that has almost 150 million base pairs in its genome. However, in the world of genetics, size is not always an advantage: although this impressive size may suggest great genetic complexity, everything indicates that it may, in fact, be a evolutionary disadvantage for the species.


Photography by Japanese Paris taken on Mount Haku in 2003.
This problem arises from the practical implications of having such a large genome. The larger it is, the more difficult and time-consuming the process of cell duplication, a truly essential aspect in the reproduction, growth and development of organisms. This difficulty can lead to a lower reproduction efficiency and, consequently, a decrease in the probability of survival of the species.
THE VIRAL LEGACY OF THE GENOME
Thus, there is no doubt that DNA is a true record of evolutionary history. In fact, everything indicates that around 8% of our genome is made up of DNA belonging to retroviruses, a class of viruses that have managed to integrate into our genetic material and persist over generations. These once infectious retroviruses have mutated over the years, becoming part of our genetic heritage.
In other words, the presence of these viruses in our genome is the result of old infections that affected cells, allowing viral genetic material to integrate into our own DNA. As these cells were duplicated and passed from generation to generation, the viral DNA was inherited along with the rest of the genome, becoming part of us.
Tags: interesting facts DNA
--