A nanoemulsion of copaiba oil (Copaifera officinalis), a plant used by indigenous people from the Amazon region to treat skin diseases, can be an ally in the fight against the zika virus, as reported by the Digital Look. Tests in vitro carried out by researchers from the Universidade Estadual Paulista (Unesp) highlighted a potential antiviral effect of the substance. But how can this work?
read more
New studies are needed to prove effectiveness
During the study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, tests confirmed the stability of the nanoemulsions for 60 days, when stored at 4° C. Furthermore, their ability to be internalized by cells infected by the virus was identified.
Subsequently, simultaneous treatments were carried out with the nanoemulsion at a maximum non-toxic concentration of 180 micrograms per milliliter (μg/mL). The results were compared with those of another formulation without copaiba oil.
A viral inhibition of 80% was observed for the version with the oil and 70% for the version without, that is, both the structure of the nanoemulsion and its association with the oil showed activity. The researchers also confirmed that higher concentrations of the substance have the capacity to inhibit viral RNA levels.
In addition to indicating paths for developing therapies for a neglected disease, it is important to highlight that it is a natural oil – and used in small quantities, which could facilitate the development of a future drug.
Marilia de Freitas Calmon, researcher at the Institute of Biosciences, Letters and Exact Sciences at Unesp
Despite the promising results, further studies are needed. This is because the oil-free nanoemulsion also showed antiviral activity, suggesting the possibility that part of the effect is related to the composition of egg lecithin (mainly phosphatidylcholine) present in the nanoemulsion structure. Other studies have even demonstrated the inhibitory capacity of lipid nanoemulsions derived from natural foods.
Furthermore, details about how Zika virus replication is inhibited are lacking. The information is from Agência FAPESP.
Zika
- Brazil is one of the countries most affected by the Zika virus.
- There were more than 250 thousand suspected cases of the disease in 2016.
- Although no deaths were recorded in 2024, probable cases increased by around 16% in the first three months of the year compared to the same period last year.
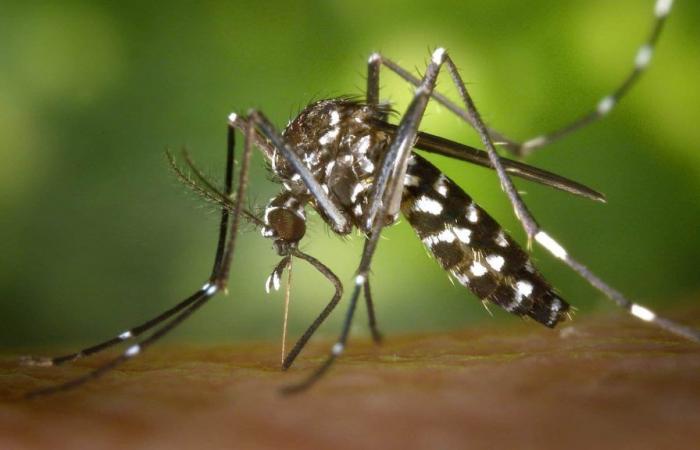
- The disease is transmitted by mosquitoes Aedes aegyptithe same as dengue and chikungunya.
- But in the case of Zika, it can cause a congenital syndrome that includes visual, auditory and neuropsychomotor changes in babies.
- In adults, it can cause neurological disorders, such as Guillain-Barré syndrome.
- To date, there are no vaccines or treatments for the infection.
- Authorities recommend that, in case of symptoms such as sudden fever, headache, pain behind the eyes, joints and body, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain, in addition to itching and red spots on the skin, the patient seeks medical attention immediately. .
Tags: indigenous plant treat viral diseases